Research And Development Initiatives Taken In The Anti-Infective Drugs Market
Pharmaceutical companies and federal governments are increasingly working together in partnerships and collaborations to provide funding and implement incentive programs for the research and development (R&D) of anti-infective drugs. These partnerships provide financial and technical assistance across different clinical development phases to pharmaceutical companies. Programs such as the Innovative Medicines Initiative’s (IMI’s) New Drugs for Bad Bugs (ND4BB) program, Joint Programming Initiative on Antimicrobial Resistance (JPIAMR), and Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority’s (BARDA) Broad Spectrum Antimicrobials Program have been implemented for the development of novel antibiotics by focusing on R&D gaps. Similarly, Global Antibiotic Research and Development Partnership (GARDP) was set up by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Drugs for Neglected Diseases Initiative (DNDi) in May 2016. This R&D initiative focuses on the development of new or improved antibiotic treatments.
On the other hand, some companies in the anti-infective drugs market are exiting the R&D pipelines of anti-infective drugs. Scarcity of new drug targets, market saturation, stringent process of regulatory approvals, and increased research and development costs are among the reasons that are compelling companies to close their R&D pipelines of anti-infective drugs. Other reasons include faster growth rate of anti-microbial resistance than the increasing rate of drug development. In July 2018, Novartis terminated its antibacterial R&D followed by Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca and Eli Lilly.
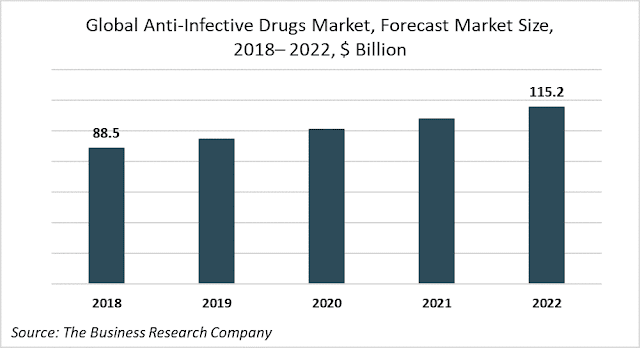
Anti-infective drugs are the medicines capable of preventing the spread of an infection by killing infectious organisms or by inhibiting the growth of disease-causing microorganisms. The global anti-infective drugs market, valued at $88.5 billion in 2018, will grow to $115.2 billion in 2022 at an annual growth rate of more than 6.5%.
The anti-infective drugs market is expected to benefit from the latest developments in drug discovery procedures such as stem cells and organ-on-chip (OOC) technologies. OOCs are micro-engineered biometric systems that simulate the activities, mechanics and physiological responses of organ systems. Drug trial processes such as target identification, validation, and screening are being executed through OOC and stem cell technologies. These technologies are considerably reducing the drug discovery costs and generating reliable predictions on drug efficiency and human safety. Another area of development is physiology-simulation modelling, in which the integrated physiology of the human organism, in both health and disease, is simulated through a computer program. Eli Lilly and Pfizer have adopted Amazon’s Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) platform to conduct simulation models in early stages of the drug discovery process that are operational within hours, whereas traditional models take weeks to conduct simulations. The wide adoption of these technologies is expected to drive the anti-infective drugs market in the forecast period.
Interested to know more about The Business Research Company?
The Business Research Company has published over 300 industry reports, covering over 2400 market segments and 56 geographies. The reports draw on 150,000 datasets, extensive secondary research, and exclusive insights from interviews with industry leaders.